Your basket is currently empty!
The International Baccalaureate offers a continuum of widely-ranging programmes for students. Find more information about the various levels below and click here to see current information about first teaching and first examination dates.
Overview of the International Baccalaureate
1. The Primary Years Programme (PYP)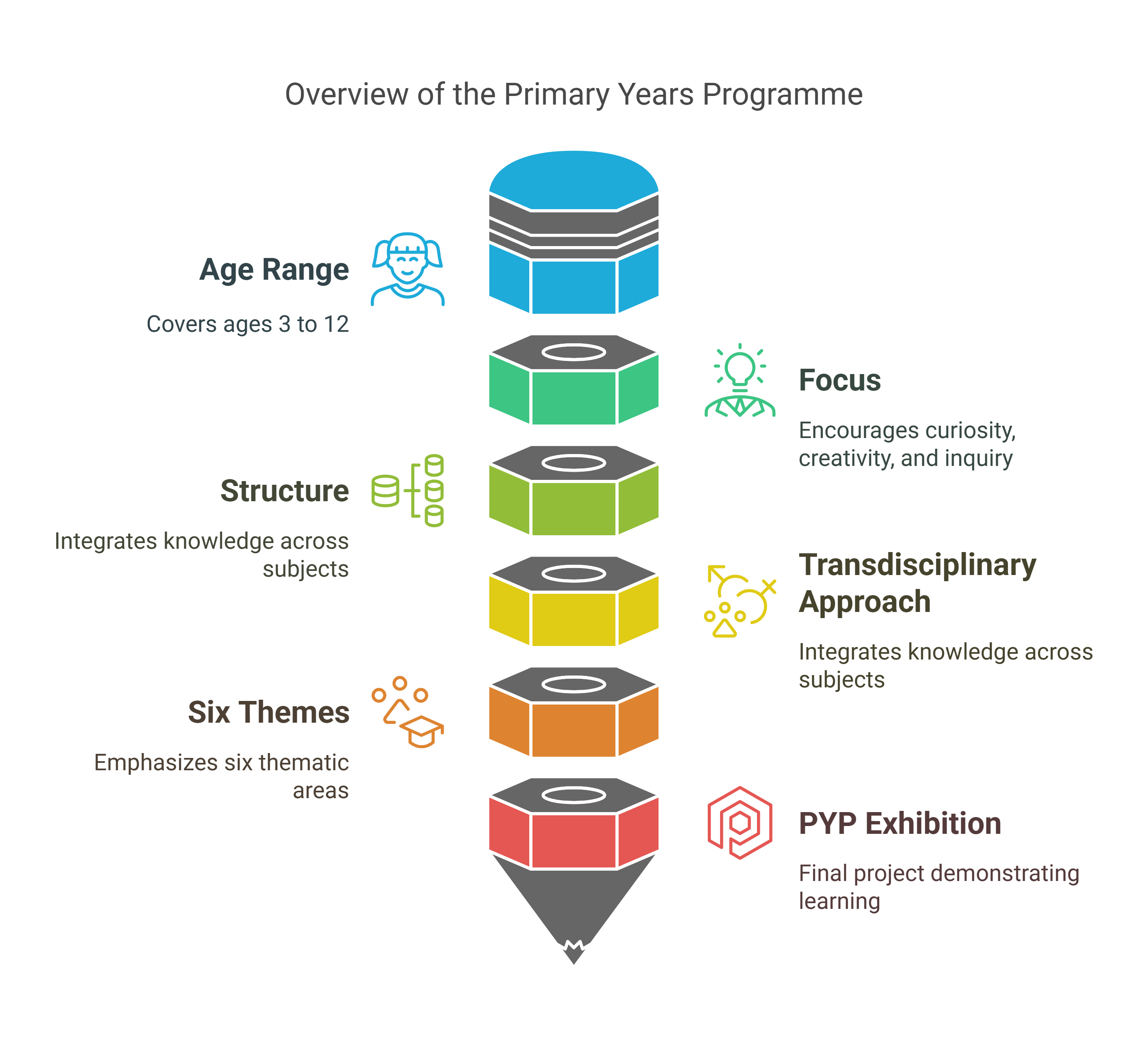
- Age Range: 3–12 years
- Focus: The PYP lays the foundation for lifelong learning by encouraging students to develop curiosity, creativity, and a sense of inquiry.
- Structure:
- Transdisciplinary approach, integrating knowledge across subjects.
- Emphasizes six themes, such as “Who we are” and “How the world works.”
- Students engage in a final project called the PYP Exhibition, where they demonstrate their learning through a collaborative inquiry.
2. The Middle Years Programme (MYP)
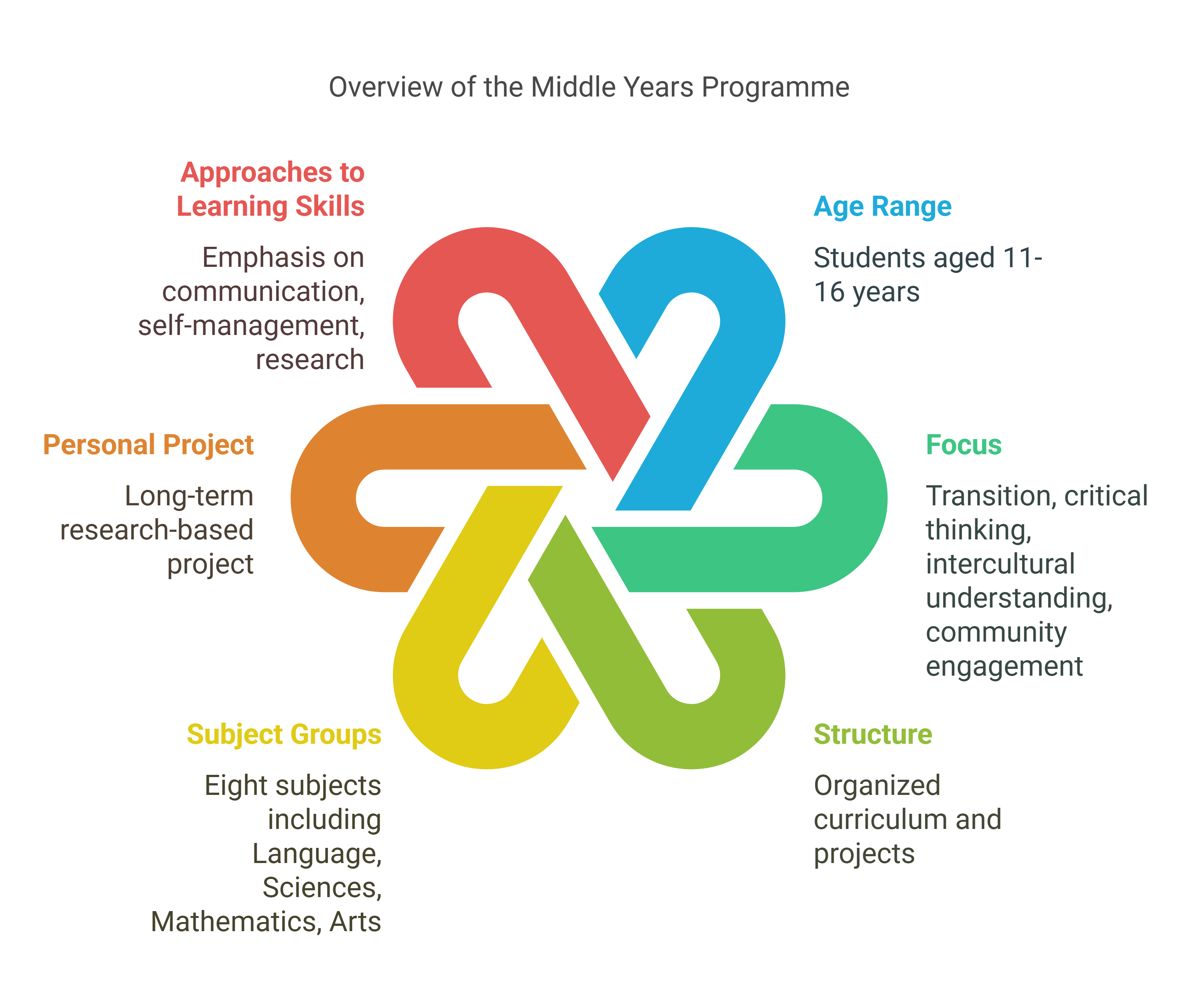
- Age Range: 11–16 years
- Focus: Bridges the transition from primary to secondary education, fostering critical thinking, intercultural understanding, and community engagement.
- Structure:
- Curriculum organized into eight subject groups, such as Language and Literature, Sciences, Mathematics, and Arts.
- Includes the Personal Project, a long-term research-based project where students explore a topic of personal interest.
- Emphasizes Approaches to Learning (ATL) skills like communication, self-management, and research.
3. The Diploma Programme (DP)
- The International Baccalaureate (IB) Diploma Programme offers students a broad
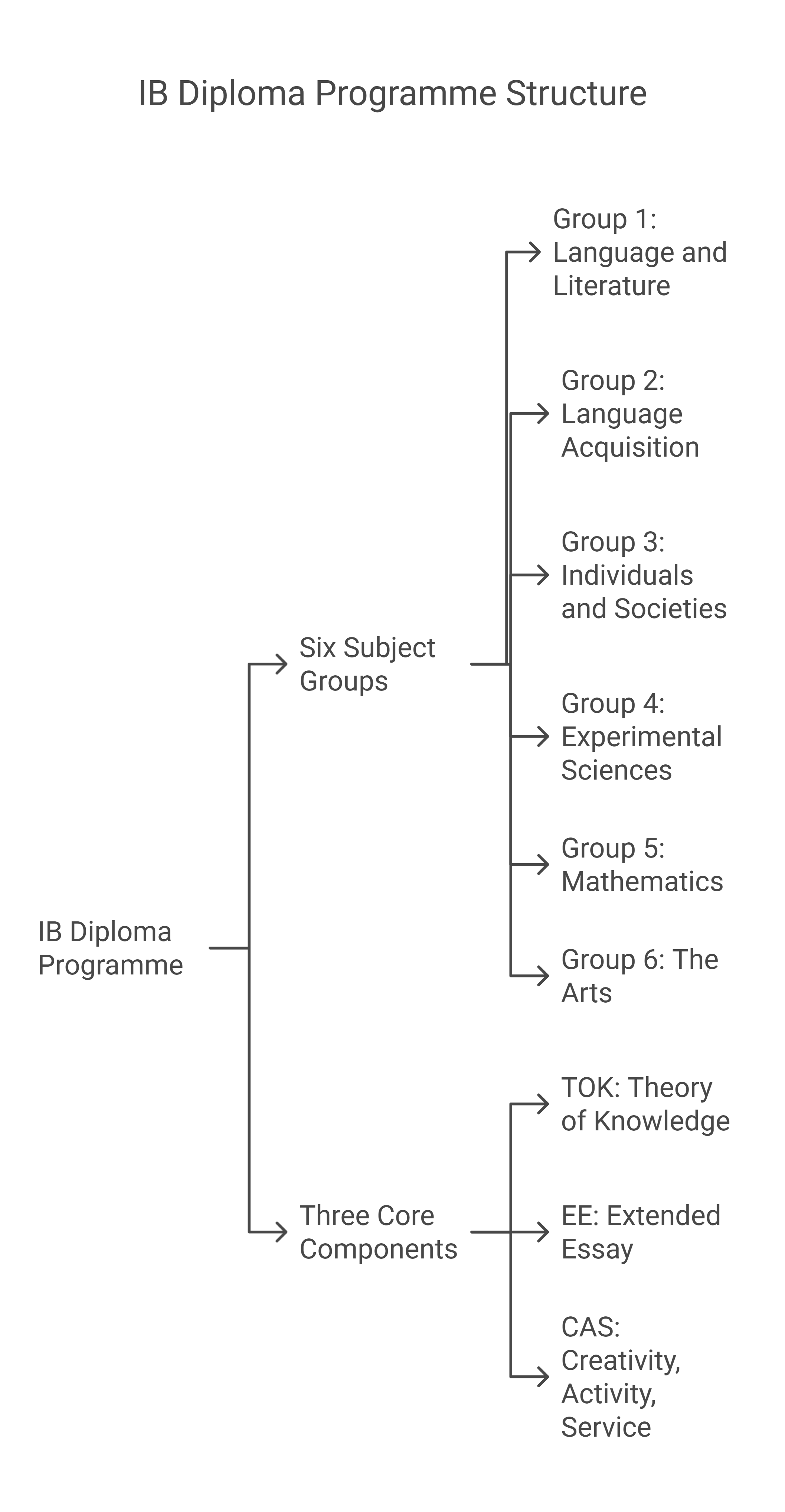 and balanced education. It requires students to choose subjects from 6 different subject groups, along with completing 3 core mandatory components. The breakdown of the subject groups and core elements are:
and balanced education. It requires students to choose subjects from 6 different subject groups, along with completing 3 core mandatory components. The breakdown of the subject groups and core elements are:
The Six Subject Groups:
- Group 1: Language and Literature
- Focus: Primarily studied in the student’s native language (e.g., English).
- Examples: English Literature, Language and Literature, etc.
- Purpose: Develops reading, writing, and analytical skills.
- Group 2: Language Acquisition
- Focus: Learning a second or additional language.
- Examples: French, Spanish, Mandarin, German.
- Purpose: Develops communication skills and cultural awareness.
- Group 3: Individuals and Societies
- Focus: Subjects related to social sciences, history, and human behavior.
- Examples: Economics, History, Geography, Psychology, Global Politics.
- Purpose: Promotes critical thinking and understanding of human societies.
- Group 4: Experimental Sciences
- Focus: Natural and physical sciences.
- Examples: Physics, Chemistry, Biology, Environmental Systems and Societies.
- Purpose: Fosters scientific inquiry and problem-solving skills.
- Group 5: Mathematics
- Focus: Different levels of mathematics.
- Examples: Mathematics: Analysis and Approaches, Mathematics: Applications and Interpretation.
- Purpose: Develops mathematical reasoning and problem-solving skills.
- Group 6: The Arts
- Focus: Creative subjects in the arts.
- Examples: Music, Theatre, Visual Arts, Film.
- Purpose: Cultivates creativity and artistic expression.
How the Subject Choices Work:
- 1 Subject from each group: Students must choose 1 subject from each of the 6 groups (one of which can be an additional subject from groups 1 to 5, if they do not want to take an art subject).
- Higher Level (HL) vs. Standard Level (SL): Students can choose 3-4 subjects at Higher Level and 2-3 subjects at Standard Level.
- HL: These subjects are studied in-depth, with a minimum of 240 hours of teaching.
- SL: These subjects are studied at a more basic level, with a minimum of 150 hours of teaching.
The 3 Core Mandatory Components:
- Theory of Knowledge (TOK)
- Focus: Explores the nature of knowledge and how we come to know things.
- Purpose: Encourages students to critically reflect on different ways of knowing and areas of knowledge.
- Extended Essay (EE)
- Focus: Independent research project on a topic of the student’s choice.
- Purpose: Develops research, writing, and analytical skills; counts as a 4,000-word essay.
- Creativity, Activity, Service (CAS)
- Focus: Engages students in extracurricular activities that promote personal growth.
- Purpose: Involves students in creative pursuits, physical activity, and service to the community.
These components are central to the IB Diploma Programme, encouraging a holistic education that combines academic rigor with personal development. The core subjects (TOK, EE, and CAS) help students apply their knowledge and foster critical thinking, while the subject groups ensure a comprehensive and well-rounded academic experience.
- Group 1: Language and Literature
4. Career-related Programme (CP)
- Age Range: 16–19 years
- Focus: Combines academic learning with career-related education for students who are more vocationally oriented.
- Structure:
- Students take a minimum of two DP courses alongside a career-related study.
- Core components:
- Personal and Professional Skills: Focuses on workplace and life skills.
- Reflective Project: Investigates an ethical issue related to their career path.
- Service Learning: Involves community-based learning.
- Language Development: Enhances linguistic proficiency in an additional language.
Summary of the Continuum
The IB continuum—PYP, MYP, DP, and CP—aims to develop well-rounded individuals who are inquirers, knowledgeable, open-minded, and reflective. Each programme builds on the previous one, ensuring a consistent and cohesive educational journey for students while allowing schools the flexibility to implement them independently or in combination.
First Teaching Dates of the Current IB Syllabus
‘First teaching’ refers to the first academic year in which a newly revised or updated syllabus for a specific subject is officially introduced to schools. It marks the beginning of the implementation phase for the revised curriculum in classrooms.
Key Points about ‘First Teaching’:
- Curriculum Review Cycle:
The IB regularly reviews and updates its subject curricula, usually on a 7-year cycle, to ensure they remain current, rigorous, and aligned with the latest developments in education and the subject matter. - First Teaching Year:
This is the year when teachers start using the updated syllabus to instruct students. For instance, if the syllabus for IB Biology is updated with “first teaching in 2025,” this means all IB schools will start teaching the revised content in the academic year beginning in 2025. - Examination Alignment:
The “first examination” for the revised syllabus typically occurs 1-2 years after “first teaching,” depending on whether it’s a Standard Level (SL) or Higher Level (HL) course. For example:- If “first teaching” is in 2025, the “first examination” might take place in 2027, allowing the students who begin the course that year to sit for the corresponding exams.
- Transition Period:
Schools may have to transition from the old syllabus to the new one during the year of “first teaching.” Teachers often undergo professional development to familiarize themselves with the updated curriculum and assessment requirements. - Relevance for Students and Educators:
- For students, it means the content and structure of their course may differ from what previous cohorts studied.
- For teachers, it requires adapting lesson plans, materials, and teaching strategies to align with the revised syllabus.
First Teaching dates for IB Subjects with their First Examination dates are:
First Teaching 2025
Computer Science: 2027
Design and Technology: 2027
Psychology: 2027
Visual Arts: 2027
Extended Essay: 2027
Career Path Core: 2027
First Teaching 2024
Environmental Systems & Societies: 2026
Global Politics: 2026
Sports, Exercise, and Health Studies: 2026
First Teaching 2023
Biology: 2025
Chemistry: 2025
Physics: 2025
Philosophy: 2025
First Teaching 2022
Business & Management: 2024
Classical Languages: 2024
Digital Society: 2024
Literature & Performance: 2024
Theatre Studies: 2024
First Teaching 2020
Economics: 2028 (next exam)
Music: 2022
Theory of Knowledge: 2022
First Teaching 2019
Mathematics: 2021
Language A: Language: 2021
Language A: Language & Literature: 2021
First Teaching 2018
Language Ab Initio: 2020
Language B: 2020
First Teaching 2017
Geography: 2019
History: 2019
Social & Cultural Anthropology: 2019
Film: 2019
First Teaching 2012
Dance: 2014
First Teaching 2011
World Religions: 2013

